Illness
by Susan Vogt
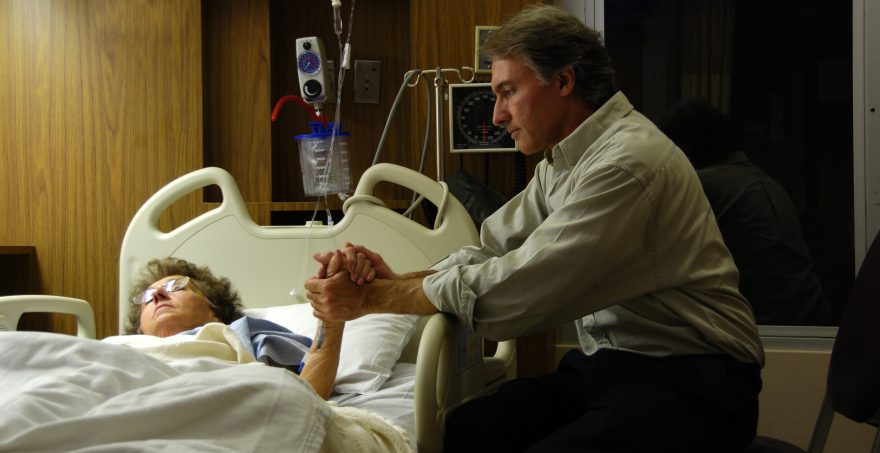
Many kinds of illness- physical, mental and emotional- can impact a marriage. They range from the occasional cold, to an unexpected accident, to chronic or terminal illness.
Here we consider long term or chronic illnesses, and serious conditions such as cancer, loss of a limb, diabetes, and life- altering disabilities. All of these test the “in sickness and in health” part of the couple’s marriage vow. Illness, especially chronic illness, changes the relationship with spouse, family, friends, social network, and God. Illness can bring out the best – and sometimes the worst – in both spouses.
A long or severe illness is usually a crisis- a turning point that can lead to ruin or renewal. A chronic or life-threatening illness creates a demand for a “new normalcy.” Not only do familiar daily patterns change, but also your expectations of how you will live, love, and share a mutual life. There is no going back to the way things were – only a going forward. At times it can feel like a roller coaster ride from hope to despair and back to hope. That’s normal. In addition to dealing with the illness itself, other issues that couples need to address include finances, ability to work, lifestyle, intimacy, and emotional and practical support for everyday life.
Dealing with the illness
This starts with understanding your illness and accessing the best medical treatment possible. Many people turn to the internet for assistance. This can be both a blessing and a curse. Which websites offer reliable help? How can you distinguish valid medical information from advertisements? See the websites below for a start. It’s crucial to have a strong network of support. Initially, many people want to help by bringing food, running errands, visiting, calling, and praying. As time goes on, however, many do not know how to give sustained help. The person with the illness and the caregiver(s) may fear asking too much or too often.
Suggestions
- Keep building your support networks as you age. Make sure you ask many people who can give at least a little time rather than depending on one or two people to do it all. Draw from church groups, neighbors, friends, relatives, community support, and support groups of persons with similar illnesses. Try to have at least five good support friends, or more, to insure that one will usually be available to lend a hand. Depending too much on the same group of people can burn out the entire group.
- Develop a mutually respectful relationship with your doctor(s). The less stress you feel about your medical care and frustration of dealing with the system, the better your chances for recovery.
- The primary caregiver needs care too. If you are the caregiver, treat yourself with as much kindness and care as you do your ill spouse.
- Take advantage of support groups for people with your illness. Look into partnering with a “patient navigator” to help you move through the medical system. Hospitals often sponsor support groups or can link you with a mentor.
Financial stressors
Some couples are blessed with insurance that covers expensive treatments when illness strikes. It may not cover lost income, however. When a wage earner loses a job, everything changes. You may need to draw down your savings and cultivate a simpler lifestyle. The illness may affect the kind of job your spouse needs to get.
If a couple is younger (especially if you are still in the active parenting stage) the financial stressors can be even greater. Some couples use up their resources and need to declare bankruptcy or hope to qualify for Medicaid.
Suggestions
- While you’re still well, consult with a person who understands the financial issues involved with chronic illness and disability. Make sure you have both a short term and long term plan.
- If it’s too late for the “while you are well” suggestion, do it now and lean on the medical support services to guide you.
Work
The loss of a job has repercussions besides loss of income. Identity is closely tied to one’s work. Work helps us feel productive, important, and useful. We may need to grieve the loss of this identity. Loss of employment also takes away important social networks. The caregiver may have to take on additional employment or household responsibilities. These role reversals can be difficult for both partners. Few people like depend on another for daily care. The ill spouse may feel guilty about burdening the caregiving spouse. Self-esteem takes a hit. Meanwhile, as generous and loving as the caregiver is, this “job” is time-consuming and draining.
Lifestyle and Recreation
The caregiver might have to do things that he or she had previously not done. The illness can become the focus of your life and everything can revolve around it: researching it, getting to/from treatment, dealing with side effects, doctor visits and support groups. Even cooking can be a challenge if the ill person needs a special diet or needs to be coaxed to eat. Recreational pursuits that both of you previously enjoyed may become physically impossible. Travel may be more difficult. This doesn’t mean you don’t have fun; you just have to be creative about finding new interests that fit changing physical abilities. Recreation may become more passive such as watching TV, movies, or going out to eat. The caregiver may need solo recreation such as working in the garden or going out with friends.
Suggestions
- Careful planning can help couples work out treatment schedules, but make peace with the reality that the future is not knowable or predictable.
- Keep a sense of humor. Make sure that each day includes some type of play and spiritual activity.
- Do not let the illness become the primary organizing principle of your life, even though recreation might not be what you’re used to. Persons who do the best in treatment are those who continue to play, take short vacations or day trips, and continue to socialize to the extent they are able.
Intimacy and sex
Physical limitations, emotional and physical fatigue, financial pressures, and lack of time can all affect intimacy and lovemaking. Snuggling may replace sexual intercourse. Sometimes, even touching or holding is difficult. Many chronically ill people report that although sexual intercourse is limited or non-existent, emotional and spiritual closeness increases because of the shared trauma. Look for new ways to express your love so that you can sustain a caring, growing relationship.
Mental Illness
A spouse with mental illness presents an even more complicated situation. The disease is harder to “see” and often caries a stigma. Relative and friends may not be compassionate. It can be hard for the caregiver if the spouse is unwilling to accept help and follow treatment. The mentally ill person may show little gratitude for the efforts of the caregiving spouse. In this situation, a support group with an effective counselor is a must.
RESOURCES:
Hanks, Jerry and de Cordova-Hanks, Bobbie. Tears of Joy. Infinity Publishing, 2006.
Stephen Ministries trains and organizes lay people to provide one-to-one Christian care to hurting people in a faith based setting.
The author acknowledges the Durham, NC Cancer Support Group for its help.
For Further Reading:
- Let me Sow Light: Living with a Depressed Spouse by Amy Viets and Bernadette Stankard
- Grieving with Grace by Dolores R. Leckey
- Every Tear will be Wiped Away by Gretchen L. Schwenker
- It Is Well: Life in the Storm by Chris Faddis
Resources for Caregivers:
- Nourish for Caregivers – a faith-based program designed to meet the practical, emotional and spiritual needs of family caregivers.
About the author
Susan Vogt is an author and speaker on marriage, parenting, and spirituality. Her website is SusanVogt.net.




